Recent Services
- Otology
- Cochlear and Hearing implants
- Nose and Sinus (Rhinology)
- Voice and Throat (Laryngology)
- Dizziness and Vertigo (Neuro-otology)
- Children (Paediatric) ENT
- Snoring and sleep-apnea
- Head and neck cancer
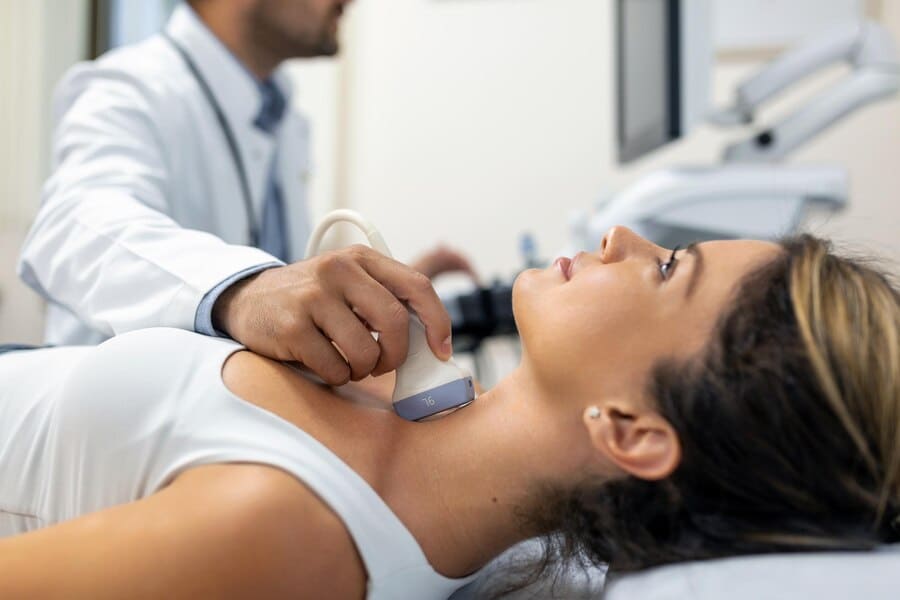
- Thyroid swelling
- Head neck swelling
- Nasal Allergy- Allergin rhinitis
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Difficulty in breathing

Thyroid swelling or goiter, is an enlargement of the thyroid gland that can appear as a lump in the neck. Symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, voice changes and a sensation of fullness. Causes vary from thyroid nodules to hormonal imbalances. Diagnosis involves physical exams, ultrasound and thyroid function tests. Treatment may include medication or surgery, depending on the underlying issue. Early evaluation and management are essential to address symptoms and prevent complications. Our clinic offers comprehensive care and personalized treatment plans to manage thyroid swelling effectively.